🌞 Build Career Success by Design
4 powerful heuristics that Max Marchione uses to navigate career uncertainty
Ello ello Earlyworkers!
Bringing career clarity into your inbox this week is Earlywork #76, a weekly cheeky newsletter sharing insights into future-focused careers for the next generation of founders & operators.
This week, we spoke with Max Marchione (Co-Founder @ Next Chapter + Investment Apprentice @ GGV) on the four most powerful heuristics he uses to design a better career.
If you’re not yet in the Earlywork community, come grow your career alongside thousands of other young people interested in tech, startups & social impact:
The Buzz 🐝
Here are the five biggest news stories across the ANZ tech & startup scene you need to know this week:
Archangel raises a $25m fund (h/t to “renowned local angel” Rayn Ong 😱)
Climate tech gets a $100m injection from superannuation funds 🌱
The secret channel to find your next job (& a cheeky Earlywork mention) 💼
Head to our #news-room in the Earlywork community to find and discuss the latest tech & startup news.
💡Weekly Cheeky Tip
Tossing up between two different career pathways?
You can never be certain about the right choice, and it looks different for everyone.
But there are a few powerful questions you can leverage to make much better career choices for who you are.
In uncovering better heuristics for career design, we spoke to Max Marchione (Co-Founder @ Next Chapter + Investment Apprentice @ GGV), who’s building a dedicated community around career clarity for high-performers.
Despite still being in uni, Max has interned in VC, investment banking, equity analysis and product management at AfterWork Ventures, Goldman Sachs, Resolution Capital and Downsizer, on top of being a founder and angel investor.
Over the past few years, these are the four most important career design principles that he’s cultivated:
Here’s the insidious myth of career design:
“You need to know what you want to do.”
Searching for career certainty is career-limiting.
Why? Searching for certainty results in:
Naively copying others and
Becoming closed off to better opportunities.
How, then, should we think about career design?
Bad news: there’s no single answer.
Instead, career design is personal. It’s about:
a) Understanding decision-making principles (which I’ll step through)
b) Understanding yourself (which is up to you).
If you came here to be told what to do, you’re in the wrong place.
But it’s my hope that you’ll get something better.
You’ll walk away with a toolbox of decision-making frameworks applicable to careers and beyond.
Let’s begin.
How to know what to focus on 👀
I’ll present four heuristics (frameworks) to help you decide what to focus on.
No heuristic is more important than another. There’s also no prescriptive way to piece them together.
Remember, career design, done right, is deeply personal. The idea is to combine these frameworks in a way that makes sense for you.
1. The ‘nature’ heuristic 🌱
Match your career to your nature.
If your career matches your nature you’ll be good at it and be energised for the long haul.
How do you match your career to your nature? My favourite guiding principle is:
“Find what feels like play to you but looks like work to others” (Naval)
The goal is to find a game that you are uniquely well-suited to playing. What’s your competitive advantage?
To find it, look for unique combinations of your interests and talents.
For example, Bill Gates is a hard-working optimist and a computer nerd. So he founded a software company.
Gordon Ramsay is a good chef and an entertaining communicator, providing the ingredients for a reality TV empire.
In my case, I’m curious and multidisciplinary, have contrarian opinions, and move relentlessly fast to improve things.
My experience is at the intersection of health and wellness, investing, real estate and community. So I’m starting a business in this space.
“The happiest people discover their own nature and match their life to it.” (Ray Dalio)
2. The ‘learning’ heuristic 🎓
Select tasks where you can learn the most.
Constant learning pays off in the long run. To get what you want, you need to deserve it.
And the trick to being ‘deserving’ is to become more talented… which is done through learning.
When I was younger, I took this to an extreme. I stopped tutoring for $150/hr to start interning for free. I prioritised learning and delayed gratification.
How can you do the same right now?
The type of learning matters too. There’s no point learning the wrong thing for 80 hours per week.
Direction – selecting “what to learn” – is just as important as the speed of learning. Start by learning the most important skill.
3. The ‘options’ heuristic 📚
Select jobs based on the options they create.
Successful people have one striking commonality: they seize the right opportunity at the right time.
From the outside, this looks like luck. But from the inside, successful people put themselves in the arena for luck to strike.
Here’s how you can do the same:
(A) When faced with two options, choose the one that creates more options, particularly early in your career.
Many people don’t realise they’re getting a lucky break in life when they get it. If a big thinker, founder, CEO, etc. suggests a meeting, cancel anything you have planned. You may not see such a window open up again.
Later in your career, you can become more selective. It’s either “hell yes” or “no”.
But here’s the kicker…
(B) You need to know when to stop pursuing optionality.
The consequence of options is that it can lead to never making the crucial decision. Optionality can backfire. Acquiring options can become an endless habit … rubber stamp after rubber stamp.
So, how do you know when to stop pursuing optionality?
When you are young, try everything, explore every job, and say yes often. Doing so allows you to find the right thing to do and the right people to work with.
But when you find these things, stop. Invest deeply. Burn the boats.
There’s a point when you need to stick with something for the long term to compound gains. That’s how compounding works. Simple.
If your dreams are apparent to you, pursue them.
4. The ‘risk’ heuristic 🚨
Select riskier jobs when you are younger.
This heuristic has two components: (A) riskier jobs, and (B) when you are younger
Let’s break them down:
(A) Why riskier jobs?
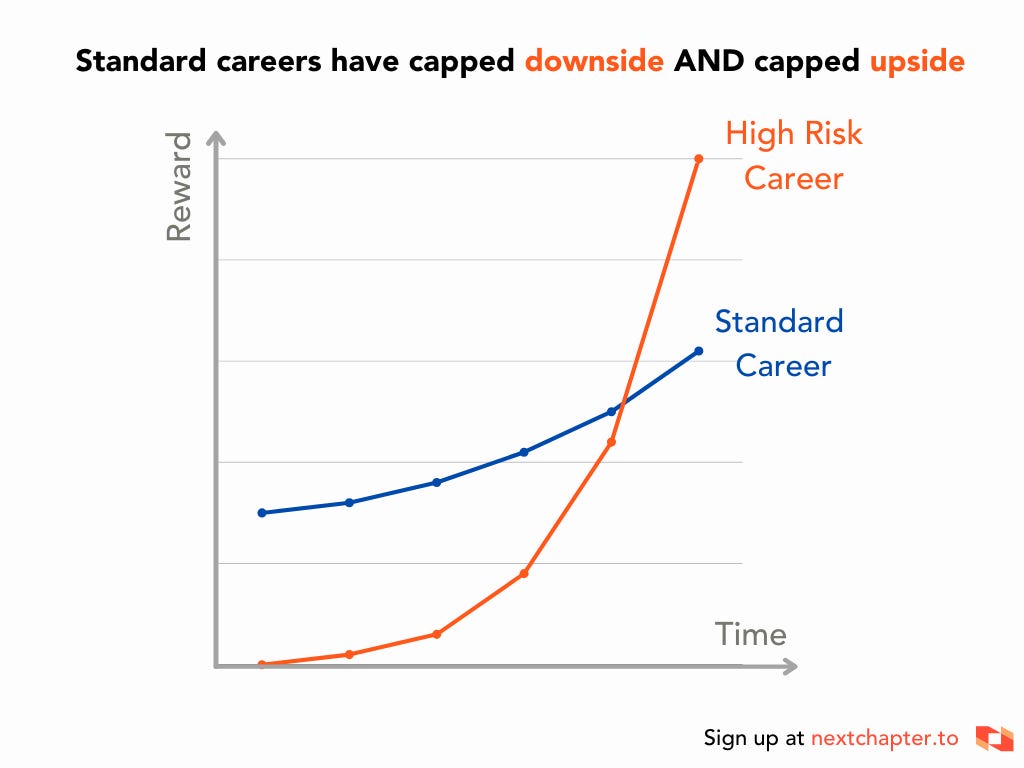
There is a positive correlation between risk and reward.
‘Standard careers’ – think consulting, banking, medicine – have capped downside. But they also have capped upside.
However, ‘non-standard careers’ – like startups, investing, and content creation – have unlimited upside.
However, the downside is larger, which brings us to:
(B) Why when you are younger?
The maximum downside is bankruptcy.
When you are 20, bankruptcy might cost you between $1,000 and $100,000.
However, when you are 40, bankruptcy might cost $1,000,000 to $10,000,000.
It takes longer to recover $1 million than $1,000. When you’re 20, without kids, you can recover quickly, allowing you to take more risks.
Finally, luck favours the one who tries.
Taking risks gives you a better chance of being lucky. If you’ve got a 25% chance of succeeding, it takes 4 tries on average to succeed.
You need to be in the arena to have a chance.
Keen to read more of Max’s work? Check out Next Chapter for curated, 2-minute career & life advice from high performers. If you’re keen to join their community, they have a new member intake currently open!
If you’re new here, welcome! Subscribe now to keep a pulse on our latest stories:
Vibed with this piece? 🍵 Shout us a cheeky herbal tea
Keen to learn more about what we do? Join the Earlyjourney and hit us up on:
🧡 Earlywork Community
🤝 LinkedIn
🐦 Twitter
📸 Instagram
🎶 TikTok
💌 Email
Ciao for now,
Team Earlywork (Dan, Jono, Marina, Jarrad & Varun)
If you’ve got a mate who would find this helpful, spread the love and share it: